People-to-people bond is the social foundation of the Belt and Road Initiative. In Vision and Proposed Actions Outlined on Jointly Building Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road, the Belt and Road Initiative will focus on people-to-people bond, which includes inheriting and carrying forward the spirit of friendship and cooperation along the Silk Road and conducting extensive cultural exchanges, academic exchanges, personnel exchanges and cooperation, media cooperation, exchanges between youth and women, and volunteer services. This will lay a solid foundation for deepening bilateral and multilateral cooperation[2]. Over the past five years, the Belt and Road Initiative has made some headway in people-to-people bond in terms of content, breadth and depth. From the perspective of the construction field, people-to-people bond has upgraded from traditional cultural exchange to social and cultural exchange covering every field. From the perspective of construction breadth, people-to-people bond has extended from projects supported by the government to projects of people's own in which all kinds of players participate extensively. From the perspective of construction depth, people-to-people bond has developed from simple social communication to all-round communication and cooperation.
The "Five Connectivity Index" of the Belt and Road Initiative Research Group of Peking University have quantitatively evaluated the progress of the Belt and Road Initiative. In 2018, the research group further optimized the indicator system and calculation method, and mainly focused on the analysis of the connectivity between China and 94 Belt and Road countries to understand the overall construction of the Belt and Road Initiative in 2017.
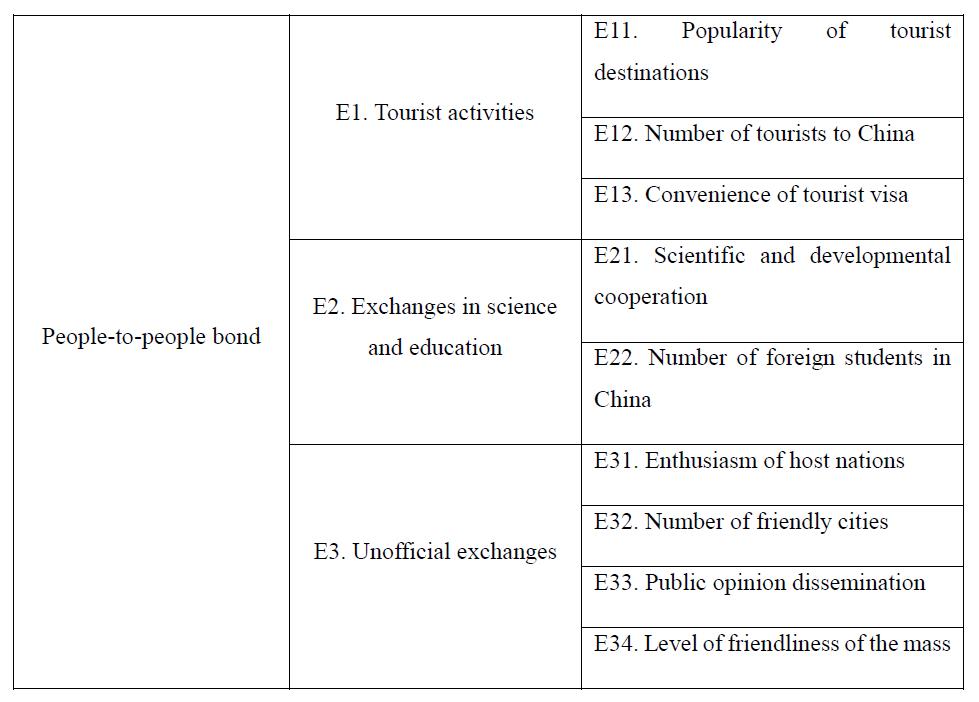
Compared with the people-to-people bond indicator system of 2017, the new indicator system of 2018 retains three Tier II indicators, namely, "tourist activities", "exchanges in science and education" and "Unofficial exchanges”, the 2018 Indicator System still retains three categories: "tourism activities", "scientific and educational exchanges" and "non-governmental exchanges". However, in Tier III indicators, the "tourist visa status" under "tourist activities" in the 2017 indicator system is updated to "tourist visa convenience"; "scientific research cooperation, Chinese institute construction and scientific and technological cooperation platform" under "science and educational exchange" updated to "scientific research cooperation and the number of foreign students in China"; "cultural exchange activities, number of sister cities and popular affection" under "unofficial exchanges" updated to "enthusiasm of host nations, Number of friendly cities, and level of friendliness of the mass". On the whole, the 2018 indicator system of people-to-people bond places more emphasis on dynamics and practicality in the light of the Belt and Road Initiative, so as to objectively and comprehensively reflect the people-to-people bond between China and Belt and Road countries.

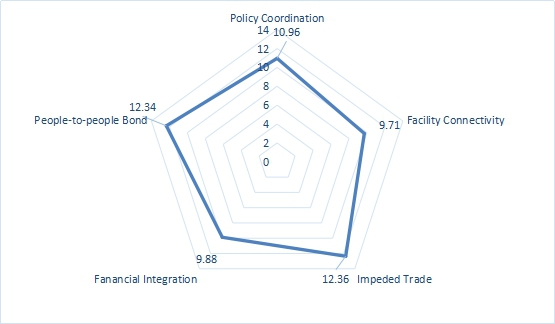
First, the construction of people-to-people bond is generally good. In 2018, the average score of people-to-people bond index reached 12.34, reaching to the level of "connected". Of all Five Connectivity Indexes, the index of people-to-people bond is at a relatively good level, ranking second on the average, only lower than the score of unimpeded trade (12.36), and higher than policy coordination (10.96), financial integration (9.88) and facilities connectivity (9.71). Overall, Five Connectivity indexes can be classified into two types: unimpeded trade and people-to-people bond fall into the category of "connected"; policy coordination, financial integration and facilities connectivity fall into the category of "good". There is little difference between the scores of each index. (See Figure 6-1)
Second, the construction of people-to-people bond is relatively balanced between regions, and the differences are large among countries within the same region. From the regional distribution, people-to-people bond indexes can be divided into three categories, namely, smooth, connected and good. Among them, Southeast Asia has the highest score, and falls into the category of "smooth". South Asia and Europe fall into the category of "connected", Central Asia and Mongolia, West Asia and North Africa and Oceania fall into the category of "good". In terms of intra-regional distribution, Europe, South Asia, West Asia, North Africa and Central Asia are relatively balanced. However, the index distribution of people-to-people bond within Southeast Asia and Eurasia is uneven. Specifically, in Eurasia, the people-to-people bond index of Russia has the highest score of 18.07, while Armenia and Moldova belong to the weak type, with only 8.72 and 7.63 scores, respectively. Of the eleven countries in Southeast Asia, seven fall into the category of "smooth", three "connected" and only Timor-Leste "weak". In Oceania, New Zealand and Australia fall into the category of "smooth", Fiji "connected", and the remaining four countries "potential". Cook Islands has the lowest score of 4.09, which is weak.


Third, science and education exchanges and tourism activities are better than non-governmental exchanges in the construction of people-to-people bond. The average scores of science and education exchange, tourism activity and unofficial activities were 4.45, 4.43 and 3.54 respectively. In science and education exchanges, Britain, Australia, Thailand and Italy have a relatively good relationship with China. However, the scientific and educational exchanges between Oceanian countries and China are relatively weak. Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Singapore, Fiji and United Arab Emirates fared relatively well in tourism activities. In terms of official exchanges, Russia, Germany, Britain, Australia and France have a relatively good relationship with China. Overall, tourism activities are relatively evenly distributed among different regions, while Oceania is relatively weak in scientific and educational exchanges and non-governmental exchanges.

After five years of development, people-to-people bond construction has reached a new stage. In 2017, China and the Belt and Road Initiative countries showed a trend of overall people-to-people bond construction, balanced regional development, relatively big intra-regional differences and relatively weak non-governmental exchanges. The reasons are as follows:
First, all-round and multi-form cultural and social exchanges have become the basis for deepening people-to-people bond. In the five years since the Belt and Road Initiative was launched, cultural exchanges, scientific and educational cooperation, tourism cooperation, and medical cooperation have become the mainstream of the Belt and Road Initiative. On the one hand, cultural exchanges, science and education cooperation and tourism cooperation have been gradually fixed and developed to a large scale. The cultural departments, enterprises and folk enthusiasts of many provinces and autonomous regions in China take the "cultural high-speed railway" to integrate and reuse rich cultural resources, create new value from the tradition, and vigorously spread the cultural spirit of the Silk Road to China and the countries along the Belt and Road.[5] In February 2017, the State Administration of Cultural Relics issued the "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan for the Development of the State Cultural Relics". The Plan proposes to enhance exchanges and cooperation with countries along the Belt and Road and international organizations on cultural heritage, and to build the Belt and Road Cultural Heritage Corridor.[6] On 20 October 2017, the Silk Road International Arts Festival Alliance was officially established in Shanghai. A total of 124 arts festivals and institutions from 32 countries and regions joined the Alliance, which is the first international art festival alliance formed by dozens of arts festivals from countries and regions along the Silk Road.[7] The year 2017 was the Year of China-Australia Tourism Cooperation. The two countries have launched a series of new measures to further promote the two-way tourism exchanges. [8]On the other hand, medical and media cooperation have become a useful complement. On January 18, 2017, the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding between the government of the People's Republic of China and the World Health Organization on Health Cooperation in the Belt and Road Initiative, has promoted cooperation with key partners along the Belt and Road. The Chinese medical team has joined hands with countries along the Belt and Road to build the "Healthy Silk Road", promoting the sustainable development of the community of shared future for mankind and becoming an important milestone in promoting global health and common development.[9] In April 2017, the Second Belt and Road Theme Day Forum was held in Beijing to tap the cultural and commercial potential of the Belt and Road Media Alliance for members of cooperation agencies, and to establish a shared communication platform to promote media cooperation among countries along the Belt and Road to a higher and newer level. [10]
Second, the degree of participation of civilians has become an important factor in the long-term development of people-to-people bond. China's folk diplomacy develops from "people's diplomacy", and gradually forms a diplomatic situation in which enterprises, political parties, social organizations and so on participate. While civil society participation in the Belt and Road Initiative is growing, in terms of the degree of participation, it is still limited compared to government-led projects. Taking the Belt and Road Network of China as an example, in 2017, there were more than 100 reports on the construction of people-to-people bond, but only about a quarter of the activities were dominated by private citizens. At the same time, according to the 2018 people-to-people bond, folk communication was a relatively weak link in the construction of people-to-people bond, and has become a factor restricting the communion of people's hearts and minds. In the long run, civil society players and their interactions are far from adequate. First of all, folk communication is a kind of communication activity with the people as the main body and initiator, which can attract public participation to the maximum extent and form a good atmosphere for communication. Second, the communicative activities dominated by folk players are more "people-friendly" and flexible than those dominated by the government. Direct contact of the people can deepen the friendship among the people, and realize "people-to-people friendship" and "heart-to-heart communication". Third, the construction of a community of shared future for mankind needs to be people-based. The construction of people-to-people bond based on good folk communication will provide the practical basis for the construction of a community of shared future for mankind.
Finally, the tradition of communication has become the restrictive factor of the regional imbalance in the construction of people-to-people bond. Oceania had a low score in the 2017 people-to-people bond index. There are 7 countries at potential or weak level in Central and Eastern Europe, 5 in Oceania, 4 in West Asia and North Africa, 4 in Europe, 2 in Eurasia, 1 in South Asia, 1 in Central Asia and 1 in Southeast Asia. It can be seen from this that the degree of people-to-people bond is closely related to the degree of diplomatic and economic exchanges between countries. In five years of practice, based on economic and political exchanges, the Belt and Road countries have formed a "comfort zone" of people-to-people bond; that is, the better the political or economic relations, the better the people-to-people bond. In countries with relatively good political and economic relations with China, existing exchanges can provide a basis for the building of people-to-people bond. For example, for the areas surrounding China, due to cultural and linguistic similarities and frequent mutual exchanges, the construction of people-to-people bond is relatively good. However, in Central and Eastern Europe and Oceania, there are still some obstacles in the construction of mutual communication between the people because of relatively less exchanges at the government level.
People-to-people bond is the most basic, solid and lasting connectivity. After five years of construction and development, the construction of people-to-people bond has achieved great results. People-to-people exchanges between Belt and Road countries and China have been increasing, and their understanding of China has also been deepening. People-to-people bond construction is a long-term and continuous process. It is not only an independent project, but also dependent on other four Connectivity. There are still some problems, including misunderstandings and obstacles, in the current people-to-people bond construction under the Belt and Road Initiative. Therefore, in order to further deepen the building of people-to-people bond, we must attach importance to "benefiting the people's livelihood", "intensive cultivation", and "friendship building".
First is "benefits". The starting point for people-to-people bond should be "benefiting the people's livelihood." At present, people-to-people bond construction has achieved good results in many fields, and exchanges and understanding among the people have been deepening. However, cultural exchange is still the mainstream of the construction. From the long-term development of the construction of people-to-people bond, only those programs that "benefit the people's livelihood" can win lasting in-depth support from the people, and become the pillar of "people-to-people friendship". Therefore, in the construction of people-to-people bond, we should take "benefiting the people" as the core content, take the needs of the people of the target country as the guidance, and take the improvement of the social environment and the people's livelihood of the target country as the goal, and vigorously carry out projects that benefit the people of the target country.
Second, in building mutual understanding among the people, we must take "intensive cultivation" as the main working method. The Belt and Road passes through numerous regions, among which cultures, languages and customs vary greatly from region to region. From the current construction practice, the main types of projects and activities are concentrated, and the contents are similar. These activities helped to open up the situation and deepen the understanding of China among the countries along the B&R in the early stages of construction. In the long run, the projects of single form and content are not conducive to the sustainable development of mutual communication between the people. Therefore, only projects emphasizing "one country, one policy" based on the "intensive cultivation" can make people-to-people bond deeply rooted in the hearts and minds of the people. There is a need to carry out a series of activities based on the social and cultural characteristics of the target country, with a sustained and humanistic concern.
And third, people-to-people bond construction should be rooted in the cultivation of friendship. With the increase of participants in the construction of people-to-people bond, the participation of all kinds of players has gradually increased. We need to deepen "friendship" with the "people's feelings" as the basic point in our exchanges. For example, during foreign communications, enterprises and social organizations, should attach importance to their friendship with the people of the target countries and deepen their friendship at the non-governmental level, so as to build a solid foundation of public opinion for the Belt and Road Initiative.
Notes:
—————————————————————
FOCUS ON CONTEMPORARY NEEDS.
Should you have any questions, please contact us at public@taiheglobal.org