On March 28th 2015, the Vision and Actions on Jointly Building Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road(Belt and Road Initiative) was jointly released by the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China. Covering three continents, China’s most comprehensive development strategy ever is expected to bring remarkable development opportunities to China and the world. This article will illustrate the opportunities as well as the challenges in the implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative.
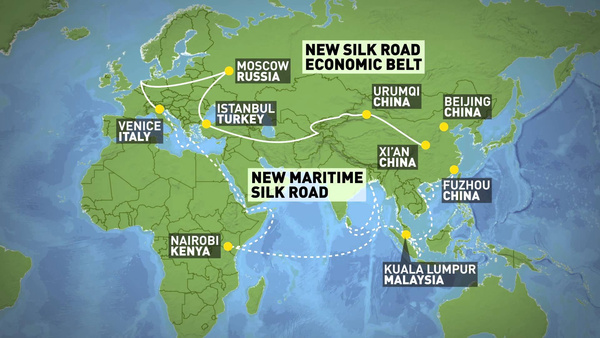
Firstly, the Belt and Road Initiative aims to rejuvenate cultural exchanges and strengthen economic links along the ancient Silk Road and Maritime Silk Road.
Secondly, the Belt and Road Initiative, as opposed to traditional economic cooperation or diplomacy, will promote the connectivity of Asian and European continents from both land and seas. More specifically, icountries along the Belt and Road in a comprehensive fashion in the five key areas, namely, t has indicated, for the future development of China, the five key points of “policy coordination, facilities connectivity, unimpeded trade, financial integration and people-to-people bond”, and shall bring great development opportunities to a wide range of industries and fields of China.
Thirdly, the Belt and Road Initiative will transform the economic cooperation between China and the outside world from based on “Made by China” and “Made in China” to “Made with China” and “Prosper with China”.
Firstly, sovereignty capital is faced with security risk. Relevant supporting policies will be required to protect China’s investment during the implementation of the strategy. The total amount and direction of investment shall be accurately considered and determined in order to protect the safety of sovereignty capital. China and the collaborating countries ought to build an effective investment protective mechanism to guarantee the safety of China’s investment and investors.
Secondly, the credibility of project appraisal needs to be improved. It should be noted that certain local governments of China or foreign governments may intentionally exaggerate the political and economic significance of their areas (or countries) so as to include in the scope of the Belt and Road their own areas (or countries).
Thirdly, the large gap among different cultures. The Belt and Road involve in a wide range of countries, which have quite different cultures, regimes and benefit appeals. Thus, the planning should seek for the high agreement among the collaborating countries and avoid distrust and suspicion.
Fourthly, it still leaves open if those industries with excess capacity would be really needed by the collaborating countries and could play meaningful and reasonable roles in those countries.
Firstly, relevant government authorities and industries should collaborate proactively with each other.
Secondly, financial institutions need to meet the requirements of all sorts of bodies. They are expected to create and develop new services and products to adapt to the new circumstances. For instance, banks may provide regular fixed asset loans and working capital loans, along with other sorts of financial supports through cooperating with trust, security, or financial leasing companies, and also they may provide support by assisting in issuing mid-to-long term notes financing or providing different types of securities.
Thirdly, the demand for talents must be met in the implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative. Talent training will always be the top priority to make the investment projects sustainable in a long term, and the so called foreign talent aid need to be done in advance. For example, China may encourage the enterprises having the intention to take part in the Belt and Road Initiative to donate to certain foundations (which may receive tax returns), and then to carry out China-foreign cooperation in running overseas schools in light of international conventions (combing with the enterprise scholarship for studying in China) to educate local talents, thereby helping Chinese companies in their cross-border investment.
Fourthly, culture communication and transmission must be more practicable without being contrived. It is necessary to find an effective and proper way to propagate Chinese culture in the world.
Fifthly, private capital should be encouraged to play its due role. It is suggested that the government offer preferential policies, supports and flexibilities to the private entities to facilitate the outward development of China’s SMEs.
—————————————————————
FOCUS ON CONTEMPORARY NEEDS.
Should you have any questions, please contact us at public@taiheglobal.org